Pregnancy is a condition when a woman should pay a special attention to the health and hygiene of her teeth and gums. We can often hear the patients say that they lost all of their teeth during the pregnancy or that the babies took all the calcium from their teeth. These statements are completely incorrect. Once incorporated into the tooth tissue, calcium cannot be reresolved and thus … be transferred into the mother`s or baby`s bloodstream.
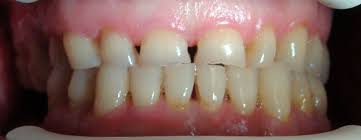
During pregnancy, women often suffer from hyperemesis gravidarium – frequent vomitting of the acid content which increases acidity on the teeth surface, as well as from heartburn, sickness and nausea, which all lead to dental hygiene neglect. This increases the number of microorganisms in the mouth and causes caries.
It has been noticed that women neglect oral hygiene during pregnancy and after baby`s birth when mothers constantly look after their babies.
Inflammatory processes on gums – gingivitis gravidarium are caused by hormonal disorders related to pregnancy. Gums are swollen, painful and bleeding. These changes let food remain around the teeth, which causes caries.

From all this we can conclude that it is primarily important to maintain oral hygiene (teeth and gums hygiene) during pregnancy, as well as to visit a dentist regularly. If you plan pregnancy, you should better have all of the teeth cavities remediated first and follow the dentist`s advice on the right oral hygiene. Our doctors are licensed to implement the ITOP oral hygiene training.
Pregnancy itself is a physiological state – not an illness, and almost all stomatological interventions can be performed painlessly. The safest period is the second trimester when all teeth should be remediated. If the pregnancy is ’risky’, the planned intervention should be approved by a gynecologist. X-ray of teeth and jaws as a usual diagnostic procedure is not performed during pregnancy and shoud be avoided as much as possible.